Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Terasaka, Yuta; Sato, Yuki; Uritani, Akira*
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 1062, p.169227_1 - 169227_6, 2024/05
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2022-065, 111 Pages, 2023/03
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust" conducted from FY2018 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for four fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop a novel alpha-ray camera consisting of imaging and an energy spectrometer to find the alpha dust to reduce the risk of health damage in decommissioning. We have developed the camera with a position resolution of less than 10  m, and the measurement test for the energy spectra was operated using several alpha-ray sources with an unfolding method.
m, and the measurement test for the energy spectra was operated using several alpha-ray sources with an unfolding method.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Nagoya University*
JAEA-Review 2022-033, 80 Pages, 2022/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2021. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station (1F), Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Measurement methods for the radioactive source distribution inside reactor buildings using a one-dimensional optical fiber radiation sensor" conducted from FY2019 to FY2021. Since the final year of this proposal was FY2021, the results for three fiscal years were summarized. The present study aims to develop an optical fiber type radiation sensor that can measure the radiation distribution one-dimensionally along the fiber under a high radiation field for the decommissioning of 1F. Based on the conventional time-of-flight method, we found several promising sensor candidates for the radiation distribution measurement under high dose rate and many scattered gamma-rays.
Hagiwara, Hiroki; Kondo, Keietsu; Hidaka, Akihide
Journal of Radioanalytical and Nuclear Chemistry, 331(12), p.5905 - 5914, 2022/12
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:53.91(Chemistry, Analytical)Hidaka, Akihide
Nuclear Technology, 208(2), p.318 - 334, 2022/02
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:65.59(Nuclear Science & Technology)The author previously proposed that the Cs bearing microparticle (Type A) may have been formed by melting and atomization of glass fibers (GF) of the HEPA filter in the SGTS due to flame and blast during the hydrogen explosion in Unit 3. If this hypothesis is correct, the Type A could contain or accompany carbon (C), that ignites spontaneously above 623 K, because of the limited time to be heated up, inclusion of C in the binder applied on the GF surface and closely located charcoal filter. As the previous studies did not focus on C, the present analyses were performed with EPMA whether the Type A contains C. The results showed that the Type A contained C originating from the binder, and non-spherical particles accompanied by the Type A and the film surrounding the Type A contained more C, which is thought to originate from the charcoal filter. These results cannot be explained by the other mechanisms proposed so far, and can be explained consistently by the author proposed hypothesis.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Tohoku University*
JAEA-Review 2021-044, 58 Pages, 2022/01
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2018, this report summarizes the research results of the "Development of high-resolution imaging camera for alpha dust" conducted in FY2020. The present study aims to develop a novel alpha-ray camera consisting of imaging and an energy spectrometer to find the alpha dust to reduce the risk of health damage in Decommissioning. We have developed the camera in FY2020, and the measurement test for the energy spectra. Moreover, the imaging test has been operated. In addition, we have also developed a high-dose-rate monitor system using novel scintillators with red/infra-red emission.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Nagoya University*
JAEA-Review 2021-033, 55 Pages, 2021/12
The Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science (CLADS), Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA), had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project (hereafter referred to "the Project") in FY2020. The Project aims to contribute to solving problems in the nuclear energy field represented by the decommissioning of the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station, Tokyo Electric Power Company Holdings, Inc. (TEPCO). For this purpose, intelligence was collected from all over the world, and basic research and human resource development were promoted by closely integrating/collaborating knowledge and experiences in various fields beyond the barrier of conventional organizations and research fields. The sponsor of the Project was moved from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology to JAEA since the newly adopted proposals in FY2018. On this occasion, JAEA constructed a new research system where JAEA-academia collaboration is reinforced and medium-to-long term research/development and human resource development contributing to the decommissioning are stably and consecutively implemented. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Measurement methods for the radioactive source distribution inside reactor buildings using a one-dimensional optical fiber radiation sensor" conducted in FY2020. We are developing a one-dimensional optical fiber radiation sensor that can estimate the radioactive source distribution "along lines" instead of "at points". To improve the conventional time-of-flight optical fiber radiation sensor for the application under high dose rate environment, basic evaluation tests were conducted using various optical fibers with different diameters and materials.
Collaborative Laboratories for Advanced Decommissioning Science; Nagoya University*
JAEA-Review 2020-063, 44 Pages, 2021/01
JAEA/CLADS had been conducting the Nuclear Energy Science & Technology and Human Resource Development Project in FY2019. Among the adopted proposals in FY2019, this report summarizes the research results of the "Measurement methods for the radioactive source distribution inside reactor buildings using a one-dimensional optical fiber radiation sensor" conducted in FY2019.
 Sr analysis
Sr analysisHorita, Takuma; Asai, Shiho*; Konda, Miki; Matsueda, Makoto; Hanzawa, Yukiko; Kitatsuji, Yoshihiro
Bunseki Kagaku, 69(10/11), p.619 - 626, 2020/10
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0(Chemistry, Analytical)We have developed a Sr adsorption fiber for rapid analysis of  Sr. The prepared Sr adsorption fiber has a Sr-extraction layer that densely retains a Sr-selective extractant, an 18-crown-6 ether derivative, on the fiber surface. Hydrophobic group-containing polymer chains embedded onto the surface of the fiber allow to form a hydrophobic phase, incorporating Sr-selective extractants. This unique surface structure provides high adsorption capacity, leading to rapid and highly efficient adsorption of Sr
Sr. The prepared Sr adsorption fiber has a Sr-extraction layer that densely retains a Sr-selective extractant, an 18-crown-6 ether derivative, on the fiber surface. Hydrophobic group-containing polymer chains embedded onto the surface of the fiber allow to form a hydrophobic phase, incorporating Sr-selective extractants. This unique surface structure provides high adsorption capacity, leading to rapid and highly efficient adsorption of Sr . The adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was 3 times higher than commercially available 18-crown-6 ether derivative-impregnated resin (Sr Resin). The equilibrium adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was comparable to the Sr Resin. The retained
. The adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was 3 times higher than commercially available 18-crown-6 ether derivative-impregnated resin (Sr Resin). The equilibrium adsorption capacity of the Sr adsorption fiber was comparable to the Sr Resin. The retained  Sr was finally determined by a GM counter. The total analysis time including the Sr adsorption and measurement was about 1 hour.
Sr was finally determined by a GM counter. The total analysis time including the Sr adsorption and measurement was about 1 hour.
Nakamura, Tatsuya; To, Kentaro; Ebine, Masumi; Birumachi, Atsushi; Sakasai, Kaoru
Proceedings of 2019 IEEE Nuclear Science Symposium and Medical Imaging Conference (NSS/MIC 2019), Vol.1, p.735 - 736, 2020/08
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.08(Nuclear Science & Technology)A large area, position-sensitive scintillation neutron detector was developed for upgrading the SENJU, time-of-flight Laue single crystal neutron diffractometer, in J-PARC MLF. The detector has a neutron-sensitive area of 512  512 mm with a pixel size of 4
512 mm with a pixel size of 4  4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A
4 mm. The detector was developed for upgrading of the SENJU instrument. The large area detector is to be installed below the vacuum tank to enlarge a covering solid angle. A  Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
Li:ZnS (Ag) scintillator and wavelength-shifting fiber technologies are employed. Each fiber channel is read out individually with photon counting mode. The electronics boards are implemented at the backside of the detector, enabling the detector depth as short as 20 cm. The detector exhibited a detection efficiency of 45% for thermal neutron. No degradation in fiber position and in neutron sensitivity has been observed over one year after production. In this paper, detector design and detector performances are presented.
Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Sakurai, Akitaka; Miyara, Nobukatsu; Sugita, Yutaka
JAEA-Research 2020-004, 68 Pages, 2020/06
In construction and operational phase of a high-level radioactive waste disposal project, it is necessary to monitor on mechanical stability of underground facility for long term. In this research, we measured the displacement of the rock around the gallery and the stress acting on support materials. Furthermore, we investigated the durability of measurement sensor installed in the rock mass and the support material such as concreate lining and steel support. As a result, optical fiber sensor is appropriate for measurement of the displacement of rock mass around the gallery, while it is enough to apply the conventional electric sensor for the measurement of stress acting on the support material in the geological environment (soft rock and low inflow). The result of the measurement in the fault zone in 350 m gallery, show that the stresses acting on both shotcrete and steel arch lib exceeded the value which will cause the instability of the gallery. However, as, we found no crack on the surface of the shotcrete. By observation on the surface of shotcrete, thus, it was concluded that careful observation of shotcrete around that section in addition to the monitoring the measured stress was necessary to continue. In other measurement sections, there was no risk for the instability of the gallery as a result of the investigation of the measurement result.
Aoki, Tomoyuki*; Tani, Takuya*; Sakai, Kazuo*; Koga, Yoshihisa*; Aoyagi, Kazuhei; Ishii, Eiichi
JAEA-Research 2020-002, 83 Pages, 2020/06
The Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) has conducted with the Horonobe Underground Research Project in Horonobe, Teshio-gun, Hokkaido for the purpose of research and development related to geological disposal technology for high-level radioactive wastes in sedimentary soft rocks. The geology around the Horonobe Underground Research Laboratory (HURL) is composed of the Koetoi diatomaceous mudstone layer and the Wakkanai siliceous layer, both of which contain a large amount of diatom fossils. Since these rocks exhibit relatively high porosity but low permeability, it is important to investigate the poro-elastic characteristics of the rock mass. For this objective, it is necessary to measure parameters based on the poro-elastic theory. However, there are few measurement results of the poro-elastic parameters for the geology around HURL, and the characteristics such as dependence on confining pressure are not clearly understood. One of the reasons is that the rocks show low permeability and the pressure control during testing is difficult. Therefore, a poro-elastic parameter measurement test was conducted on the siliceous mudstone of the Wakkanai formation to accumulate measurement results on the poro-elastic parameters and to examine the dependence of the parameters on confining pressure. As a result, some dependency of the poro-elastic parameters on confining pressure was observed. Among the measured or calculated poro-elastic parameters, the drained bulk modulus increased, while the Skempton's pressure coefficient, and the Biot-Wills coefficient in the elastic region decreased with the increase in confining pressure. The measurement results also inferred that the foliation observed in the rock specimens might impact a degree of dependency of those parameters on confining pressure.
Tamura, Koji*; Toyama, Shinichi
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai-Shi ATOMO , 62(5), p.268 - 271, 2020/05
, 62(5), p.268 - 271, 2020/05
The laser cutting technology is expected to be a promising candidate for the decommissioning measure of nuclear facilities, because it has a lot of advantage such as its high controllability and excellent suitability to remote handling by robot arm, etcetera. This report describes the recent result from laser cutting technology development for thick steel materials summarizing the cutting demonstration of 300 mm thick steels and dummy pressure vessel, the analysis of cutting condition of thick steel cutting, the observation of cutting process, remote controlled cutting system, the cutting in pile of steels by the system, and countermeasure for fume produce by cutting process.
Ito, Chikara; Naito, Hiroyuki; Ishikawa, Takashi; Ito, Keisuke; Wakaida, Ikuo
JPS Conference Proceedings (Internet), 24, p.011038_1 - 011038_6, 2019/01
A high-radiation resistant optical fiber has been developed in order to investigate the interiors of the reactor pressure vessels and the primary containment vessels at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. The tentative dose rate in the reactor pressure vessels is assumed to be up to 1 kGy/h. We developed a radiation resistant optical fiber consisting of a 1000 ppm hydroxyl doped pure silica core and 4 % fluorine doped pure silica cladding. We attempted to apply the optical fiber to remote imaging technique by means of fiberscope. The number of core image fibers was increased from 2000 to 22000 for practical use. The transmissive rate of infrared images was not affected after irradiation of 1 MGy. No change in the spatial resolution of the view scope by means of image fiber was noted between pre- and post-irradiation. We confirmed the applicability of the probing system, which consists of a view scope using radiation-resistant optical fibers.
Wakaida, Ikuo; Oba, Hironori; Miyabe, Masabumi; Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Tamura, Koji; Saeki, Morihisa
Kogaku, 48(1), p.13 - 20, 2019/01
By Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy and by related resonance spectroscopy, elemental and isotope analysis of Uranium and Plutonium for nuclear fuel materials and in-situ remote analysis under strong radiation condition for melt downed nuclear fuel debris at damaged core in "Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station", are introduced and performed as one of the application in atomic energy research field.
Shimizu, Kenichi*; Koike, Yuki*; Yamada, Taiki*; Oharada, Kazuya*; Tanaka, Keisuke*; Shobu, Takahisa
Zairyo, 65(9), p.657 - 664, 2016/09
The internal stress in crystalline thermoplastics, polyphenylene sulphide (PPS), reinforced by carbon fibers of 30 mass% was measured by the diffraction method using synchrotron with energy of 12.3 keV. The stress in the matrix was determined by the sin2psi method with side-inclination optics of transmitted X-ray diffractions. Using skin-layer strips cut parallel, perpendicular and 45 degree to the molding direction of the injection molded plates, the matrix stress was measured under the uniaxial applied stress. The experimental values were at least qualitatively agreed with the prediction derived based on micromechanics. The quantitative difference between experiment and prediction is mainly due to the neglect of the distribution of fiber orientations in the micromechanics prediction. These residual stresses were caused by the mismatch of the thermal expansion coefficient between matrix and fibers.
Sanada, Yukihisa
Kogaku, 45(8), p.300 - 305, 2016/08
For the purpose of environmental radiation measurement, decontamination effect and detection of leakage of radionuclide plastic scintillation fiber (PSF) had been used for the wide area as technique to measure radiation distribution quickly after the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant accident that occurred in March, 2011. The PSF can easily measure radiation distribution due to position sensing of radiation source. The PSF was used for the measurement before and after the decontamination by considering features that PSF obtained many point data at one time. The PSF was used for the measurement of radiocesium concentration in sediment of irrigation pond by considering features that PSF has high water resistance. This paper described the principle of PSF and the application example after the accident at the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant.
 -synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scattering
-synuclein studied by quasielastic neutron scatteringFujiwara, Satoru; Araki, Katsuya*; Matsuo, Tatsuhito; Yagi, Hisashi*; Yamada, Takeshi*; Shibata, Kaoru; Mochizuki, Hideki*
PLOS ONE (Internet), 11(4), p.e0151447_1 - e0151447_17, 2016/04
Times Cited Count:24 Percentile:64.99(Multidisciplinary Sciences) :
: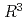

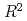
Sakurai, Daisuke; Saeki, Osamu*; Carr, H.*; Wu, H.-Y.*; Yamamoto, Takahiro*; Duke, D.*; Takahashi, Shigeo*
IEEE Transactions on Visualization and Computer Graphics, 22(1), p.945 - 954, 2016/01
Times Cited Count:5 Percentile:41.49(Computer Science, Software Engineering)Scalar topology in the form of Morse theory has provided computational tools that analyze and visualize data from scientific and engineering tasks. Contracting isocontours to single points encapsulates variations in isocontour connectivity in the Reeb graph. For multivariate data, isocontours generalize to fibers inverse images of points in the range, and this area is therefore known as fiber topology. However, fiber topology is less fully developed than Morse theory, and current efforts rely on manual visualizations. This paper therefore shows how to accelerate and semi-automate this task through an interface for visualizing fiber singularities of multivariate functions  :
: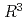

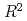 . This interface exploits existing conventions of fiber topology, but also introduces a 3D view based on the extension of Reeb graphs to Reeb spaces. Validation of the interface is performed by assessing whether the interface supports the mathematical workflow both of experts and of less experienced mathematicians.
. This interface exploits existing conventions of fiber topology, but also introduces a 3D view based on the extension of Reeb graphs to Reeb spaces. Validation of the interface is performed by assessing whether the interface supports the mathematical workflow both of experts and of less experienced mathematicians.
Verzilov, Y. M.; Nishitani, Takeo; Ochiai, Kentaro; Kutsukake, Chuzo; Abe, Yuichi
Fusion Engineering and Design, 81(8-14), p.1477 - 1483, 2006/02
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:17.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English